Seasonal Tax Deductions: What to Consider
/Summer has begun, and its arrival heralds the commencement of the festive season. In the spirit of Holiday cheer, many businesses are marking the approaching close of the 2025 calendar year with gifts and events for clients and staff. To maintain compliance with tax regulations set out by the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) during your celebrations, there are a few things to consider when planning business parties and purchasing employee or client gifts. Want to stay in the loop with my regular newsletter?
Each month I share business, bookkeeping, and QiBalance updates.
Is It Considered Entertainment?
Business owners who want to avoid paying Fringe Benefits Tax (FBT) and who want to claim the expenses against business income may wish to avoid spending money on food, drink or recreation that are considered entertainment.
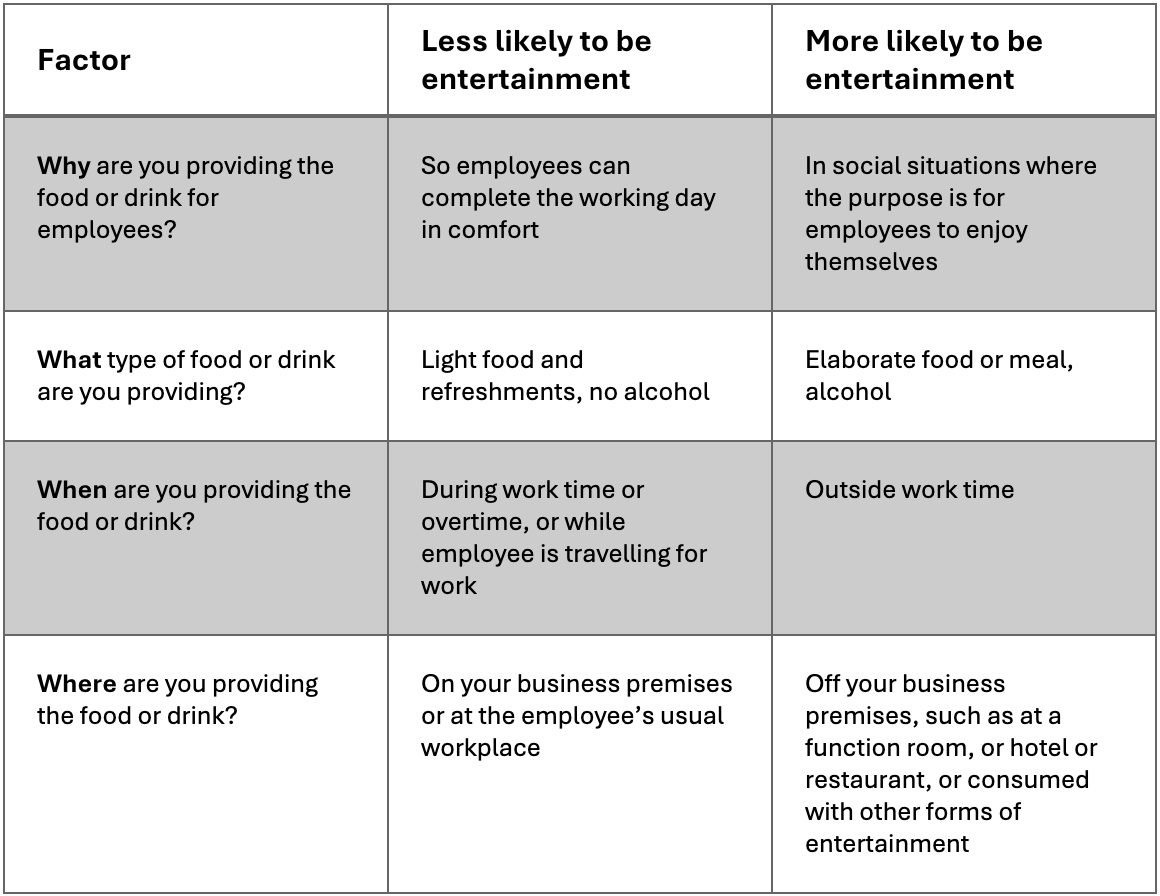
When is food or drink considered entertainment?
The Australian Taxation Office provides four factors—see below—for businesses to use to determine if food or drink provided to staff are considered entertainment. The most important factors are ‘why’ and ‘what’.
When is recreation considered entertainment?
Recreation activities that are considered entertainment include amusement, sport and similar leisure activities. Some examples are:
Golf games
Gym memberships
Theatre or movie tickets
Harbour cruises
Accommodation and travel in connection with entertaining clients or employees [1]
If food, drink or recreation expenses do not qualify as entertainment, they may be claimable as business expenses for tax purposes.
Does Fringe Benefits Tax Apply?
Fringe Benefits Tax (FBT) is a tax that employers may be required to pay on benefits provided to employees or to employees’ family or other associates. Gifts and entertainment benefits can be considered benefits for FBT purposes. Therefore, to avoid FBT liability, businesses should consider the following:
Does a Minor Benefits Exemption Apply?
Central to the concept of Fringe Benefits is the concept of Minor Benefits Exemption (MBE). MBE applies where:
the value is less than $300 including tax, and
it is unreasonable for it to be treated as a Fringe Benefit. [2]
Generally speaking, something is more likely to be considered unreasonable to treat as a Fringe Benefit if:
it is not a frequent or regular expense
the total cumulative value of minor benefits provided is not high
it is not practical to determine the taxable value
the circumstances of the benefit do not imply that it that it could be considered primarily as compensation for work provided. [2]
For more information, see the ATO page on Minor Benefits Exemptions.